| |
ITALY: EMILIA-ROMAGNA
1.
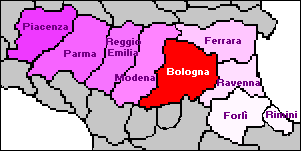
Italy - Region Emilia Romagna - Province of
Bologna
The Province of Bologna has a surface area of 370,244 square km,
with a total population of over 900,000 inhabitants. It is
administratively
divided into 60 Municipalities:
2.
List of the "Comuni" of the
Province
- Anzola dell'Emilia
- Argelato
- Baricella
- Bazzano
- Bentivoglio
- Bologna
- Borgo Tossignano
- Budrio
- Calderara di Reno
- Camugnano
- Casalecchio di Reno
- Casalfiumanese
- Castel d'Aiano
- Castel del Rio
- Castel di Casio
- Castel Guelfo di Bologna
- Castel Maggiore
- Castel San Pietro Terme
- Castello d'Argile
- Castello di Serravalle
|
- Castenaso
- Castiglione dei Pepoli
- Crespellano
- Crevalcore
- Dozza
- Fontanelice
- Gaggio Montano
- Galliera
- Granaglione
- Granarolo dell'Emilia
- Grizzana Morandi
- Imola
- Lizzano in Belvedere
- Loiano
- Malalbergo
- Marzabotto
- Medicina
- Minerbio
- Molinella
- Monghidoro
|
- Monte San Pietro
- Monterenzio
- Monteveglio
- Monzuno
- Mordano
- Ozzano dell'Emilia
- Pianoro
- Pieve di Cento
- Porretta Terme
- Sala Bolognese
- San Benedetto Val di Sambro
- San Giorgio di Piano
- San Giovanni in Persiceto
- San Lazzaro di Savena
- San Pietro in Casale
- Sant'Agata Bolognese
- Sasso Marconi
- Savigno
- Vergato
- Zola Predosa
|
| Source:
http://www.italyworldclub.com/emilia/bologna/
|
3.
EMILIA-ROMAGNA - BACKGROUND:
| The name
Emilia-Romagna comes from the Roman history. Emilia derives from
the name of Marcus
Aemilius Lepidus under who's consulate was built the road via
Emilia between Piacenza and Rimini. Romagna remembers the division
of the territory in VI century: to the north-east - the land of
Lombards (Longobardia); to the south-east - the land of Romans
(Romania). So modern Romagna is a historical region and includes
provinces of Ravenna and Forli', plus the zone of Imola in the
province of Bologna. The rest of the territory belongs to Emilia. |
| Area: 22 123 sq.km
(8628 sq.miles) (7.3%), population 3 940 000 inhabitants (6.8%),
density 178 inhab./sq.km. |
- The first settlements appeared
in the Neolithic and Iron ages on the banks of the rivers. Later
came Ligurians, Celts, Etruscans and Umbrians. The first
systematic arrangement of the territory was conducted by Romans
who made this region a fortified base between Italy and Gaul.
Here was traced the road via Emilia along which were built the
most important cities, except Ravenna and Ferrara.
- After Romans the greatest part of
the territory was conquered by Lombards; only Ravenna and Forli'
still belonged to eastern Roman empire, Ravenna became even a
capital of it, and the territory around these cities was called
Romania, later modified into Romagna.
- Thanks to the geographical
position and rich agricultural resources this region nearly for
all of its history was quite prosperous.
|
 |
- In the times of Renaissance here
took place the great urbanistic revolution, by the order of
Ercole I d'Este the architect Biagio
Rossetti projected the "new" Ferrara, called
"the first modern city of Europe". But the
transformation of the territory touched not only the cities, but
the country sides as well. Here were built numerous irrigation
channels, introduced new plants and etc.
- In times of pontifical government
the region suffered from a long crisis till 1860, the year of
annexation of Emilia-Romagna to Italy. Since then the work of
improvement of the land organization continued. This time were
involved not only the plain zones but also the mountain and the
hill parts, where 65 % of territory was adapted to cultivation
and use. Here were built the aqueducts, power lines,
methane pipelines, roads and highways. At the same time took
place the development of industry and tourism.
- Thus, the region of Emilia-Romagna
is considered to be one of the best places to live in Italy.
|
- 4.
|
- History of
Emilia-Romagna
|
- Man and
Territory Economy and Resources
|
- Archeology and
Art
|
- Origins
|
In the II
millenium b.C. Emilia-Romagna was already inhabited. In V-VI
centuries b.C. here came the Etruscans and Gauls. |
The
Etruscans had founded Felsina and created numerous commercial
centers which had the exit to the sea in the zone called Spina,
modern Comacchio. |
|
- Roman Epoch
- (from II
century b.C.)
|
Romans
defeated Gauls and settled in the region. |
Opened the
via Emilia and founded some of the colonies (Rimini, Ravenna,
Piacenza). |
|
- Middle Ages
- (V - XV
centuries)
|
In V
century Ravenna became the capital of the eastern Roman Empire; the
Lombards invaded the north-western part of the region; the
south-eastern part remained under Byzantines. During the XII century
Bologna assumed great power. |
After
barbaric invasions in XI century the work of territory improvement
continues. Creation of passageways through the Apennines.
Development of commerce and artisan activities. In XIV century
Bologna is noted for its University, production of wool; Ferrara
became famous for the tapestry production. |
Basilica of
San Vitale and church of Sant'Apollinare Nuovo in Ravenna (VI
century); the cathedral of Modena (XI century, Wiligelmo) and of
Parma (XII century, Antelami). |
- Renaissance
- (XV - XVI
centuries)
|
The period
of maximum splendour of the court of Este in Ferrara and Modena and
of Farnese in Parma and Piacenza. Bologna and Ravenna became
pontifical legations. |
|
Urbanistic
arrangement of Ferrara by the architect B.Rossetti. Palazzo Ducale
in Modena. |
- Modern Epoch (XVII=XVIII)
|
In 1796 the
French occupied the region which became the part of Cispadane
Republic (and later of Cisalpine Republic). |
New
progresses in communication system. |
|
- XIX - XX
centuries
|
After the
congress of Vienne in 1815 the previous souvereigns were restored.
In 1860 the region joined the new state of Italy. |
In the
second half of the XIX century were built the new roads and
railways. After the WWII began the intensive industrialization
favoured by the presence of capital and continued construction of
ways of communications. The start of touristic boom on the Adriatic
seacoast. |
|
- 5.
Position.
- Emilia-Romagna is one of the most extended
regions of Italy; it is limited by
the Adriatic, the Apennines and Po.
Borders on Lombardy and Veneto
(north), Liguria and Piedmont
(west), Tuscany and Marche (south),
the Adriatic Sea (east). Between Romagna and Marche the little independent
Republic of San Marino is
located.
- 6.
Climate.
- There are three climates presented in
Emilia-Romagna. In the plain
zones the climate is continental (cold and
foggy winters, hot and humid summers);
in mountain zones the climate is
of Alpine type (cold and foggy winters and
cool summers);
in the seaside
zones the climate is moderate with cold winds from north-east.
- Bologna
- January: -0.4 C
- July: 23 C
- Altitudes
- plain: 48%
- hill: 27%
- mountain: 25%
- 7.
Landscape.
- The mountain part of the region are poor
of fertile lands and vegetation,
while the plain zones introduce one of
the most animated landscapes of
the northern Italy. Here predominates
little and medium private agricultural
businesses, as well as big
companies with a great number of employees,
and cooperatives.
- The region is rich of rivers (Po, Trebbia,
Nure, Arda, Taro, Parma, Enza,
Secchia, Panaro, Reno, Rubicone,
Marecchia, Conca) most of which are
born in the Apennines.
- 8.
Communications.
- The main communication ways are via Emilia,
the ancient Roman tract.
Parallel to it go a railway and a highway;
because of its position the region
is obliged to serve as a transit
between Northern and southern Italy.
Ravenna is an important sea port
with a notable traffic of goods thanks to
developed industrial
production. There are two airports, the most important
one is in Bologna
and the second is in Rimini used in summer period for
international
charter flights.
- Tourism
- Total: 42 400 000
- Italians: 75%
- Foreigners: 25%
- Employment
- agriculture: 7%
- industry: 35%
- commerce,
- tourism: 58%
- 9.
Agriculture and breeding.
- The agriculture in Emilia-Romagna is one
of the most progressive in Italy
organized with the limited usage of
working hands and with modern technical
equipment. The principal
cultivated growings are: corn, maize, sugar beet,
fruits (peach,
strawberry, cherry, pear, apple, apricot, plum); vegetables.
The
breeding of cattle is on the second place in Italy after Lombardy.
Here
is very well developed the production of wines a big part of which
is
exported to the United States. The fishing is also notable
(1/5 of
national fish product).
- 10.
Industry.
- Emilia-Romagna is the only Italian region
which projected its development
according to the very precise model
concentrated on little and
medium private business and cooperatives.
Here was denied to build
big industrial complexes with the exception of
two chemical plants in
Ferrara (Montedison) and in Ravenna (Anic). The
basic productions
apart from those traditional (transformation of
agricultural and breeding
products) are: metal-mechanics (production of
Ferrari in Maranello),
textile, clothing, chemical, glass,
pharmaceutical, furniture and
construction materials; high technological
mechanics and electronics.
- Hydroenergy Italy:
- 44 000 000 kWh
- Emilia-Romagna:
- 1 100 000 kWh
- Thermoenergy Italy:
- 128 000 000 kWh
- Emilia-Romagna:
- 8 200 000 kWh
- Births (per 1000)
- Italy: 9.9
- Emilia-Romagna: 6.8
- Deaths (per 1000)
- Italy: 9.3
- Emilia-Romagna: 11.1
- Remnant
- Italy: 0.6
- Emilia-Romagna: -4.3
- 11.
Population.
- The distribution of the population in the
region is very balanced,
none of the urbanistic centers has got
predominating demographic
or other functions. The important commercial
and industrial center
as Bologna has only 1/9 of the population of
Emilia-Romagna.
- The second aspect is a tendency to
increase of the population,
but it is not due to the birth-rate which is
even lower than mortality,
but to the fact of greater number of
immigrants than of emigrants.
- 12.
Life.
- Emilia-Romagna is a rich region, it is on
the 3rd place after Lombady
and Valle d'Aosta by the product per
inhabitant. In the rate of the
richest cities of Italy Bologna is the
1st, Parma is the 5th, Ravenna
is the 8th, Modena is the 9th, Reggio
Emilia is the 11th. Emilia-Romagna
is on the 4th place by the
consumption of goods and services per inhabitant.
Women and men here
live longer lives than an average Italian.
The percent of people with
University degree in this region is the
highest in northern Italy; and
it is the 3rd in Italy by the number of school
graduates. The quality of
life is high (see the tables below).
Here the number of crimes is
inferior to the average Italian
rate and the lowest in central-northern
Italy.
- Inhabitants per car
- Italy: 2.0
- Emilia-Romagna: 1.7
- Expenses for sport/recreation
- (liras per inhabitant)
- Italy: 48 500
- Emilia-Romagna: 95 700
Monthly income per inhabitant
1 632 000 It.Liras
(816 US Dollars)
- 13.
Provinces and communes.
- The region is divided in eight provinces:
Bologna, Ferrara,
Forli', Modena, Parma, Piacenza, Ravenna, Reggio
nell'Emilia,
and Rimini with 341 communes.
14.
אמיליה
|
חבל טבעי
ואדמיניסטראטיבי
באיטליה
הצפונית.
נקרא כך
מתקופת
אוגוסטוס
קיסר על שם
דרך-אמיליה,
העוברת בו.
השם הרשמי
כיום הוא
אמיליה-רומניה.
החבל כולל
את המחוזות
פורלי, רונה,
פררה,
בולוניה,
מודנה, רג'ו
נל אמיליה,
פרמה ופיצ'נצ'ה.
שטחו בערך 22
קמ"ר, מהם כ 55%
בשפלה
שמדרום
לנהר פו ו 45%
בהרי
האפנינים.
גבולו של
החבל בצפון
זולת לאורך 60
ק"מ, הוא הפו,
במזרח
הגבול הוא
הים
האדריאטי,
בדרום
ובדרום
מערב: עפ"ר
פרשת-המים
הראשית
שבאפנינים.
רק בצפון
מערב אין
לאמיליה
גבול טבעי
האפנינים
שבתחום
אמיליה
מתרוממים
רק בנקודות
מועטות
למעלה מ 2000
מטר. השיא
הוא מונטה צ'ימונה:
2163 מטר, מדרום
למודנה.
עמקי-נחלים
מרובים
שיורדים
לפו או לרנו,
נהר שיוצא
מן
האפנינים
ופונה
בשפלה
מזרחה,
מרחיבים את
שטח הישוב
לתוך ההר.
בכמה מהם יש
מעברים
לעבר
האפנינים.
החשוב שבהם
הוא המעבר
בעמק-הרנו,
שבו עוברת
מסילת
הברזל
בולוניה-פירנצה,
קו התחבורה
העיקרי בין
איטליה
הצפונית
והתיכונית.
מציאותן של
שש מערי-הבירה
של מחוזות
אמיליה
לרגלי ההר
מעידה על
החשיבות
הכלכלית
והצבאית של
המעברים
בהרים ושל
הקשר בין
השפלה להר
רוב
התושבים
באמיליה
מתפרנסים
מחקלאות.
התעשיה
מעבדת את
התוצרת
החקלאית
ואת תנובת-הרפת
לצרכי החבל
והמדינה.
לגבינות
אמיליה, שהן
ידועות
בשוק בשם
גבינות
פארמה, שם
טוב גם מחוץ
לאיטליה. כן
יש באמיליה
תעשיות של
משי, לכה,
זכוכית,
מכונות
חקלאיות
ומכוניות
הסטוריה
בחלוקת
איטליה ע"י
אוגוסטוס
נקבעה
אמיליה
כאזור
השמיני.
בקיסרות
המאוחרת, מן
המאה ה 2
ואילך, היתה
אמיליה אחד
מארבעת
המחוזות
המשפטיים
של איטליה.
עד 395 לסה"נ
היוותה
אמיליה עם
ליגוריה
פרובינציה
קונסולארית
אחת. מאז
ואילך היתה
מחוז עצמאי.
בזמנו של
דיוקלטיינוס,
ואפשר עוד
בזמנו של
מארקוס
אורליוס,
ניטלה ממנה
רוונה,
שחזרה אליה
בסוף המאה ה 4
ונעשתה עיר-הבירה
שלה. עם
פלישת
הלאנגובארדים
בשנת 568,
נחרבה
מודנה, אך
שינויים
מכריעים
בהקפו של
החבל לא באו
עד המאה ה 13,
כשבולוניה
וחבליה
הרומאניה
ניתנו
לאפיפיור ע"י
אוטו
הרביעי
בשנת 1201,
ופרידריך
השני בשנת 1213.
בימי ממשלת
הלאנגובארדים
פרחו
התרבות
וההשכלה
במנזרים של
אמיליה, אך
השלטון היה
בידי
רוזנים
חולונים. רק
במאה ה 10
העניקו
המלכים
האיטלקיים
את שלטון
הערים
לאפיסקופים,
שהיה להם
חלק ניכר
בפילוג
הכנסיה
במאה ה 11.
כתוצאה
מנצחון
האפיפיור
של רומי
נתפתח
באמיליה
שלטון
בורגני,
שבראשו
עמדו
קונסולים.
ערי אמיליה
השתתפו
במאות ה 12 וה 13
בליגה
הלומבארדית.
ידה של
מפלגת
הגולפים
היתה על
העליונה
בכל הערים
משנת 1266, אך
ריב-משפחות
פילג את
המנצחים
והביא לידי
התהוותן של
הסיניוריות;
לסוף
השתלטו שתי
סיניוריות:
משפחת
ויסקונטי,
ששלטה
בפארמה
ובפיאצ'נצה,
ומשפחת ד'אסטה,
ששלטה
במודנה
וברג'ו.
בעקבות
המלחמות
בין צרפת
וספרד,
שנערכו
באיטליה
במאה ה 16,
השתלט
האפיפיור
בחבל
אמיליה,
ולחשיבות
עלו משפחות
דוכסים
אחרות.
תולדות
החבל היו
מאז, עוד
יותר משהיו
קודם לכן,
תולדות
הערים שבו |
|
| מקור:
האנציקלופדיה
העברית, כרך
ג', עמודים 962-963 |
|
|
|